The conservator tank is the main part of the transformer, It provides space for the expansion of oil and acts as a reservoir for transformer oil.
In this article, we will explore the construction, function, and working principle of the conservator tank of transformer. We will also discuss different types and their advantages.

Table of Contents
Function of the Conservator Tank
The main function of the conservator tank of transformer is to provide adequate space for the expansion of oil inside the transformer.
When the transformer is loaded and the winding and core temperature rises, this increased temperature dissipates into insulating oil, and the volume of oil increases.
The conservator tank allows the expanded transformer oil to occupy the space, preventing excessive pressure build-up in the main tank. And acts as a reservoir for transformer insulating oil.
Construction of the Conservator Tank
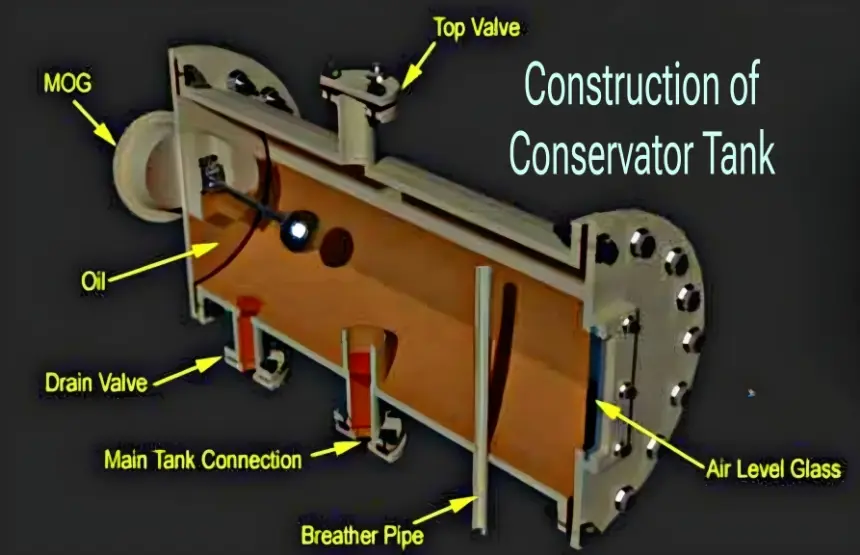
The conservator tank of transformer is a cylindrical container that is closed from both ends. It is typically mounted on the top of the transformer main tank.
The it is designed with one large inspection cover on either side, allowing easy access for maintenance and cleaning.
A conservator pipe, connected to the main transformer tank, enters the conservator from the bottom.
The head of the conservator pipe inside the conservator tank is equipped with a cap to prevent the entry of oil sludge and sediment.
Silica gel breather fixing pipes are usually positioned at the top inside the tank to ensure that oil does not enter into the breather, even at the highest operating levels.
Silica Gel Breather
Function of Silica gel breather is to maintain the quality of transformer insulating oil.
These breathers contain silica gel, which absorbs moisture from the air.
Moisture ingress can degrade the performance of the transformer and reduce the dielectric strength of the oil.
Silica gel breathers help prevent moisture ingress, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the transformer.
Regular monitoring and replacement of the silica gel are essential to maintain its effectiveness.
Oil Level Indicator
Oil level indicators monitor the oil level inside the transformer tank.
Accurate readings of the oil level are important for determining the health and performance of the transformer.
The oil level indicator should be properly calibrated and regularly checked to ensure accurate readings.
Any abnormality in the oil level can indicate a potential issue with the transformer, such as oil leakage or insulation failure.
Timely detection of such issues can prevent further damage and ensure the safe operation of the transformer.
Working Principle of the Conservator Tank
The working principle of the Conservator tank of transformer is based on the expansion and contraction of transformer insulating oil due to load and ambient temperature changes.
When the volume of oil increases, the expanded oil occupies the vacant space above the oil level inside the conservator.
This displacement pushes the corresponding quantity of air out through the breather. Conversely, when the load decreases and the ambient temperature decreases, the oil contracts, causing outside air to enter the tank through the breather.
Types of Conservator Tank of Transformer
Atmoseal Type Conservator
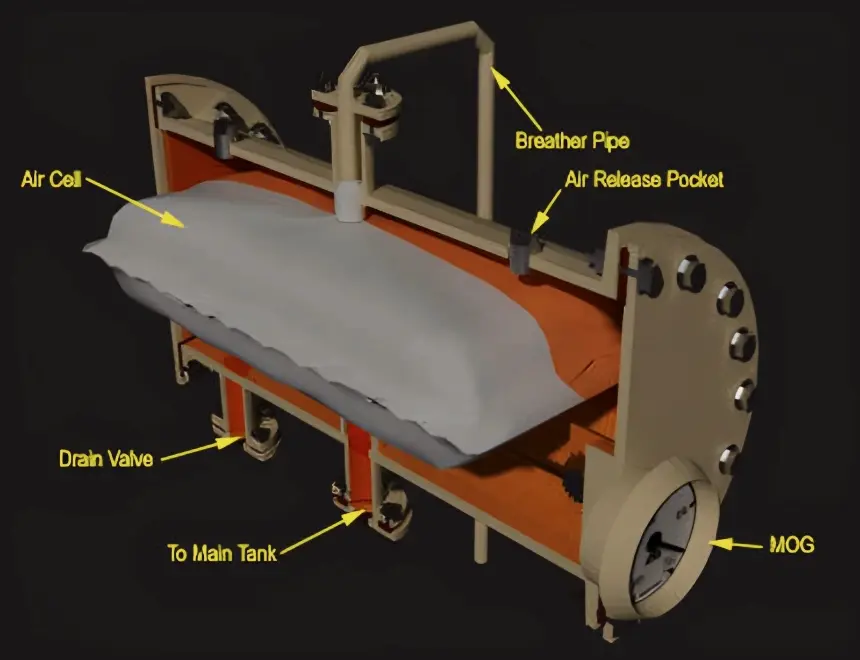
In the Atmoseal type conservator, an air cell made of NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber) material is fitted inside the conservator reservoir.
The silica gel breather is connected to the top of this air cell.
The oil level in the power transformer rises and falls depending on the deflation and inflation of the air cell.
When the air cell deflates, the air inside is released through the breather. Conversely, when the cell inflates, outside air enters through the breather.
This design prevents direct contact between the oil and air, reducing the aging effect of the oil.
Diaphragm Sealed Conservator
The diaphragm sealed conservator uses a diaphragm as a barrier between the transformer oil and atmospheric air.
This type of tank is designed with two semicircular halves, with a diaphragm held between them.
As the oil expands, it pushes up the diaphragm, which is indicated by the oil level indicator.
When the oil level decreases, the diaphragm deflects, allowing atmospheric air to enter through the silica gel breather.
This type of conservator tank has an advantage over the air cell conservator in preventing insulation failure caused by gas bubbles.
Advantages of Conservator Tanks
- It provides space for oil expansion, preventing damage to the transformer due to excessive pressure.
- it acts as a reservoir for insulating oil, ensuring a constant supply for proper insulation.
- Conservator tanks with air cells or diaphragms prevent direct contact between the oil and air, reducing the aging effect of the oil. This helps prolong the lifespan of the transformer.
- It prevents the entry of moisture and contaminants into the transformer during the breathing process.
Maintenance
- Regular maintenance of conservator tanks is important to ensure their proper functioning.
- This includes periodic inspection of the tank for any signs of leakage, corrosion, or damage.
- The silica gel breather should be checked regularly and replaced if necessary to maintain its effectiveness in preventing moisture ingress.
- The oil level indicator should be calibrated and monitored to ensure accurate readings.
Conclusion
The conservator tank is a crucial component of a transformer, providing space for oil expansion and acting as a reservoir for insulating oil. Its construction, function, and working principle are crucial for properly operating and maintaining transformers. Understanding the different types, such as the Atmoseal type and diaphragm sealed type, helps in selecting the most suitable design for specific transformer applications. Regular maintenance, including monitoring the silica gel breather and oil level indicator, ensures the longevity and reliability of the transformer.
What is a Conservator Tank in a transformer?
It is a part of a transformer that is mounted on top of the main tank and stores transformer oil. and connected to the main transformer tank through a pipe.
What is the purpose of the conservator tank?
The main purpose is to provide space for the expansion and contraction of the transformer oil due to temperature variations and load changes.
What are the types of transformer conservator tanks?
There are two types of transformer conservator tanks
1)Atmoseal Type Conservator
2)Diaphragm Sealed Conservator
