The Direct-On-Line (DOL starter) is one of the simplest and most widely used methods for starting electric motors. It is commonly employed for small to medium-sized motors where the high inrush current during startup does not cause significant issues. This article provides a detailed explanation of the DOL starter, including its construction, working principle, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
Table of Contents
What is a DOL Starter?
A DOL starter is an electrical device used to start and stop an electric motor by directly connecting it to the power supply. It applies full voltage to the motor terminals during startup, which results in a high starting current. Despite its simplicity, the DOL starter is highly effective for motors that do not require controlled starting or reduced starting current.
Construction of a DOL Starter
The DOL starter consists of several key components that work together to start, run, and protect the motor. These components include:
Contactor

- The contactor is an electromechanical switch that connects the motor to the power supply.
- It has three main power contacts (for a 3-phase motor) and a coil that, when energized, closes the contacts.
- Auxiliary contacts (NO and NC) are used in the control circuit for latching and interlocking.
Overload Relay

- The overload relay protects the motor from overheating due to excessive current.
- It consists of a bimetallic strip or electronic sensors that trip the circuit if the current exceeds a preset value.
- It is connected in series with the motor and interrupts the power supply during overload conditions.
Start and Stop Buttons
- The start button is a normally open (NO) push button that energizes the contactor coil.
- The stop button is a normally closed (NC) push button that de-energizes the contactor coil.
Fuses or Circuit Breakers
- These components provide short-circuit protection.
- They disconnect the circuit in case of a fault, such as a short circuit or excessive current.
Control Circuit
- The control circuit operates at a lower voltage (e.g., 24V or 110V) for safety.
- It includes the start and stop buttons, contactor coil, and overload relay contacts.
Power Circuit
- The power circuit connects the motor to the main power supply through the contactor.
- It carries the full load current of the motor.
Working Principle of a DOL Starter
The DOL starter works by directly connecting the motor to the power supply during startup. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of its operation:
Initial State (Motor Off)
- The contactor coil is de-energized, and the main contacts are open.
- The motor is disconnected from the power supply.
Pressing the Start Button
- When the start button is pressed, the control circuit is completed, and current flows through the contactor coil.
- The contactor coil is energized, closing the main contacts and connecting the motor directly to the power supply.
Motor Starting
- The motor receives full voltage from the power supply, causing it to start and accelerate to its rated speed.
- The inrush current during startup is high (typically 6-8 times the full load current), but it lasts only for a short duration.
Motor Running
- Once the motor reaches its rated speed, it operates normally.
- The contactor remains energized as long as the start button is held or a latching circuit keeps the coil energized.
Pressing the Stop Button
- When the stop button is pressed, the control circuit is interrupted, and the contactor coil is de-energized.
- The main contacts open, disconnecting the motor from the power supply.
- The motor stops running.
Overload Protection
- If the motor draws excessive current due to overload, the overload relay trips.
- The relay opens the control circuit, de-energizing the contactor coil and disconnecting the motor from the power supply.
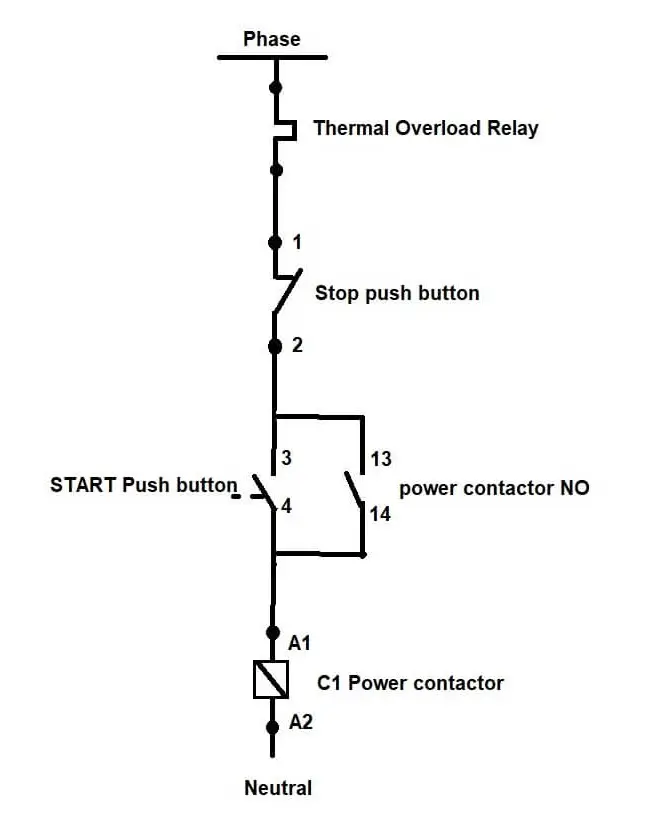
Wiring Diagram of a DOL Starter
Here’s a simplified representation of the wiring:
Power Circuit:

Copy
Power Supply (3-Phase) → Fuses/Circuit Breaker → Contactor → Overload Relay → Motor
Control Circuit:
Start Button (NO) → Stop Button (NC) → Contactor Coil → Overload Relay Contacts

Advantages of a DOL Starter
- Simple Design: The DOL starter is straightforward and easy to understand.
- Cost-Effective: It is inexpensive compared to other motor starters.
- Full Torque at Startup: The motor starts with full torque, making it suitable for applications requiring high starting torque.
- Easy Installation and Maintenance: The DOL starter is easy to install and requires minimal maintenance.
- Compact Size: It occupies less space compared to other starters.
Disadvantages of a DOL Starter
- High Inrush Current: The motor draws a high starting current, which can cause voltage dips in the power supply.
- Mechanical Stress: Sudden application of full voltage can cause mechanical stress on the motor and connected equipment.
- Unsuitable for Large Motors: The DOL starter is not recommended for large motors due to the high starting current.
- Limited Control: It does not provide controlled starting or speed control.
Applications of a DOL Starter
The DOL starter is commonly used in applications where the motor size is small, and the starting current does not cause significant issues. Some typical applications include:
- Small water pumps.
- Fans, blowers, and compressors.
- Conveyors and small machinery.
- Agricultural equipment.
- Light industrial machinery.
Comparison with Other Starters
| Feature | DOL Starter | Star-Delta Starter | Soft Starter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starting Current | High (6-8 times full load) | Reduced (1/3 of DOL) | Controlled and reduced |
| Starting Torque | Full torque | Reduced torque | Adjustable torque |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Small motors | Medium to large motors | Motors requiring smooth start |
The Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter is a simple, cost-effective, and reliable method for starting small electric motors. While it has limitations, such as high inrush current and mechanical stress, it remains a popular choice for applications where these factors are not critical. Understanding its construction, working principle, and applications is essential for selecting the right motor starter for your needs.