Master Trip Relay is an important auxiliary relay in power system protection.
In this article we will discuss, the working, function, and significance of the Master Trip Relay, also known as the 86 relay.
We will explore the different types of Master Trip Relays, their classifications, and their specific applications in power systems protection.
Additionally, we will discuss the importance of these relays in providing isolation between protection relays and circuit breakers, reducing the complexity of wiring, and enhancing the reliability of the protection system.
Table of Contents
What is a Master Trip Relay?
A Master Trip Relay is an auxiliary relay that acts as isolation between the protection relays and the circuit breaker trip coil in a power system. written as the ANSI Code 86,
Unlike protection relays, which sense faults, the Master Trip Relay is responsible for receiving input signals from various protection relays and giving the tripping command to the circuit breaker.
This relay is connected with the circuit breaker trip coil and serves as the final relay in the chain that triggers the trip command to the circuit breaker. Its primary function is to provide isolation between the protection relays and the circuit breaker’s trip coil.
Significance of Master Trip Relay (86)
The Master Trip Relay (86) holds significant importance in power system protection.
Let’s explore the key reasons why this relay is an indispensable component:
Isolation between Protection Relays and Circuit Breaker
Directly wiring protection relays to the trip coil of a circuit breaker can result in the burning of protection relay contacts in case of a fault. Since protection relays can be expensive, it is not advisable to connect them directly to the trip coil.
The Master Trip Relay serves as a protective measure by providing isolation between the protection relays and the circuit breaker’s trip coil, ensuring the safety and longevity of the protection relays.
Lock Out Relay Simplifies Wiring Complexity
Using a Master Trip Relay reduces the complexity of wiring in a protection circuit. Without a Master Trip Relay, all trip contacts of the protection relays would need to be individually wired to the circuit breaker’s trip coil.
This would lead to an extensive network of wiring, increasing the chances of DC voltage leakage and compromising the reliability of the protection system. By employing a Master Trip Relay, only two wires are required to connect to the tripping coil, simplifying the overall wiring process and reducing costs.
Multiple Contacts for Interlocking and Signaling
The Master Trip Relay is equipped with multiple contacts that can be utilized for interlocking purposes, such as tripping other breakers, as well as for annunciation and signaling to PLC or SCADA systems.
These contacts enable efficient coordination and communication within the power system, enhancing its overall performance and safety.
High-Speed Tripping Relay
The Master Trip Relay is designed as a high-speed auxiliary tripping relay, capable of issuing a trip command to the circuit breaker’s trip coil almost instantaneously.
With a nominal operating time of 10 milliseconds at the rated voltage, this relay ensures swift response and minimizes any potential damage or disruption caused by faults in the power system.
No Need for Anti-Pumping Circuit
In circuit breakers that lack an anti-pumping circuit, directly wiring protection relays with the circuit breaker’s trip coil is not feasible.
The anti-pumping circuit interrupts the tripping command once the breaker is tripped. However, with the Master Trip Relay, there is no need for an anti-pumping circuit in the circuit breaker. The relay releases a single pulse for tripping, eliminating the requirement for additional circuitry and simplifying the overall design.
Working of Master Trip Relay (86)
The Master Trip Relay (86) operates by receiving a trip signal from any of the connected protection relays.
Upon receiving the trip signal, the relay issues a single pulse trip command to the trip coil of the circuit breaker, initiating the tripping process.
Lock out relay 86 acts as the central command unit for all the connected protection relays, coordinating their actions and ensuring the circuit breaker is tripped promptly in the event of a fault.
To better understand the working of the Master Trip Relay, let’s examine its block diagram:
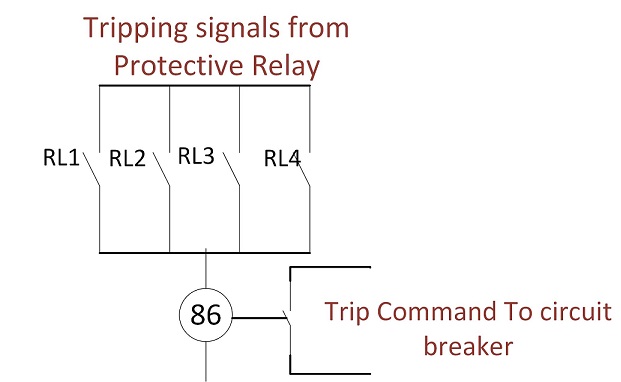
The block diagram illustrates the flow of signals and commands within the Lock out Relay, depicting its role as the central control unit for tripping the circuit breaker.
The relay’s wiring diagram further showcases its connections to the circuit breaker’s trip coil:
The wiring diagram demonstrates how the Master Trip Relay is interconnected with the circuit breaker’s trip coil, establishing the necessary circuit for issuing tripping commands.
This configuration ensures efficient and reliable tripping of the circuit breaker in response to fault conditions.
Classification of Master Trip Relay
Master Trip Relays can be classified into three categories based on the level of fault detection and their specific applications. Let’s explore each category in detail:
- Low-Level Trip lock out relay(86L)
The Low-Level Trip relay, designated as ANSI Code 86L, is primarily used for tripping auxiliary circuit breakers. In the presence of a fault with a low fault level, this relay does not trip the entire power network. Instead, it outputs a signal for annunciation purposes, alerting the operators or control systems about the fault condition. The 86L relay provides a level of fault detection that allows for early detection and appropriate action while avoiding unnecessary tripping of the entire power system. - Medium-Level Trip (86M)
The Medium-Level Trip relay, identified by the ANSI Code 86M, plays a important function in protecting the power system when the generator is running in synchronization with the grid supply. In situations where faults such as overcurrent, instantaneous overcurrent, and earth faults occur at the grid supply, the generator must be isolated from the grid supply to prevent further damage. The 86M relay performs this function by first tripping the grid breaker and, if the fault level remains high, subsequently tripping the generator breaker. Additionally, the 86M relay is responsible for tripping the generator breaker in case of mechanical failures in the generating station equipment, such as low oil pressure, low auxiliary cooling water flow, or low main cooling water pressure. The relay not only triggers the necessary tripping actions but also provides annunciation alarms to indicate the occurrence of these faults, ensuring prompt response and protection of the power system. - Heavy Trip (86H)
The Heavy Trip relay, denoted by the ANSI Code 86H, is designed to handle faults with a high magnitude that may cause severe damage to electrical and mechanical equipment. This relay, also referred to as the Lock Out relay, is wired with the turbine, grid breaker, and generator breaker tripping circuits. When protection relays detect faults such as instantaneous earth faults, restricted earth faults, standby earth faults, differential relay faults, or turbine-side faults, the 86H relay issues a trip command to the associated equipment, including the generator breaker, grid breaker, and turbine. The purpose of the 86H relay is to swiftly isolate and protect the power system from faults that pose significant risks to its operation and equipment. Additionally, the relay provides annunciation alarms to notify operators or control systems about the occurrence of these critical faults.
Resetting the Master Trip Relay
The Master Trip Relay can be reset if the fault condition no longer persists. Once the fault is resolved or cleared, the Master Trip Relay can be reset to its normal state, ready to respond to any future fault occurrences. Resetting the relay allows for the restoration of normal power system operation and ensures that the protection system is ready to respond to new fault conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Lock Out Relay (86) is an essential component in power system protection, serving as the interface between protection relays and circuit breakers.
It provides isolation, simplifies wiring, and enhances the reliability of the protection system.
The Master Trip Relay operates swiftly and efficiently, issuing tripping commands to circuit breakers in response to fault conditions. Its classification into low-level, medium-level, and heavy-level relays allows for targeted fault detection and appropriate actions, ensuring the safety and integrity of the power system. Understanding the working, function, and significance of the Master Trip Relay is crucial for professionals in the field of power system protection, enabling them to design and implement effective protection schemes and safeguard electrical networks against potential faults and hazards.

