While selecting an induction motor, Motor Duty Cycle must be considered to meet the induction motor application requirement. The duty types are indicated on motor nameplate data by S1, S2…
In the absence of an indication of the rated duty class, continuous running duty is assumed when considering a motor operation.
What Are Motor Duty Cycle?
Table of Contents
| S1 | Continuous running duty |
| S2 | Short-time duty |
| S3 | Intermittent duty |
| S4 | Intermittent duty with starting |
| S5 | Intermittent duty with starting and electrical braking |
| S6 | Continuous operation periodic duty |
S1-Continuous running Motor Duty Cycle
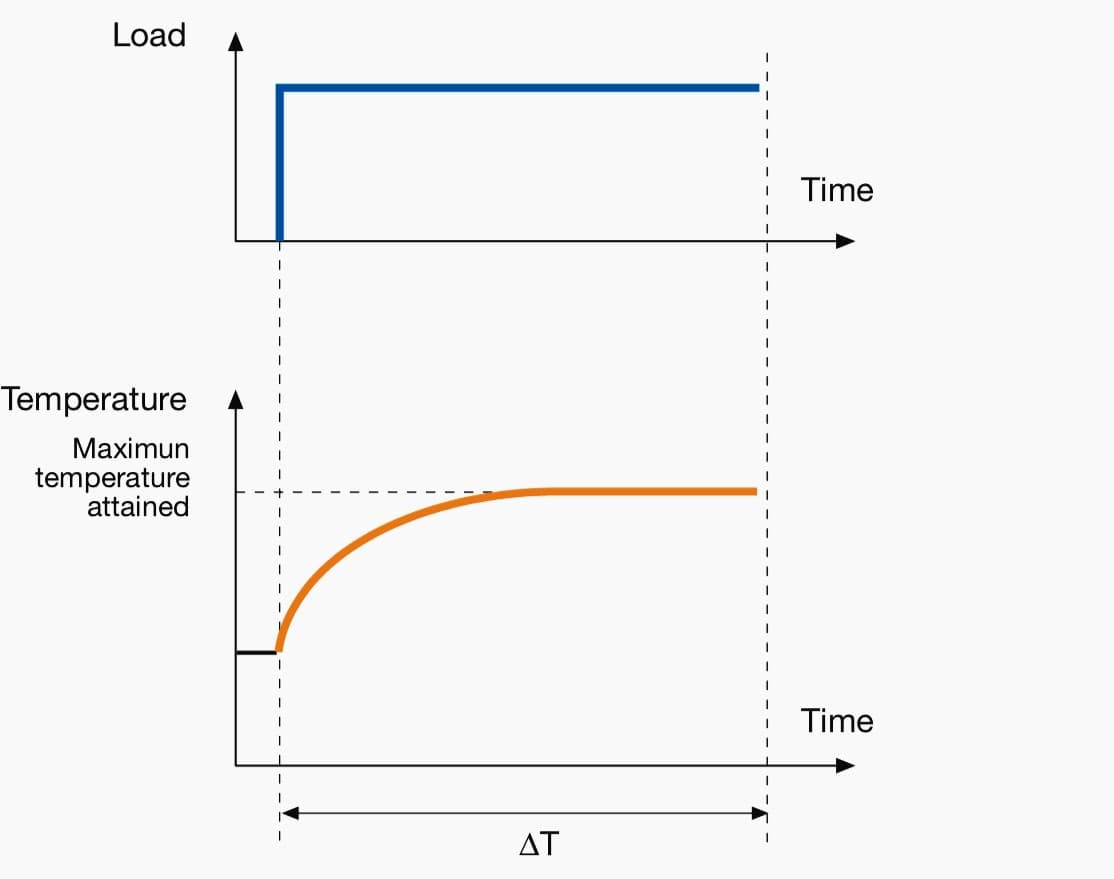
The most common type of motor duty cycle is a continuous-duty motor and is denoted by S1.
S1 Type duty induction motors Operate at a constant load for a longer duration so that it reaches thermal equilibrium.
S2 Short-time duty
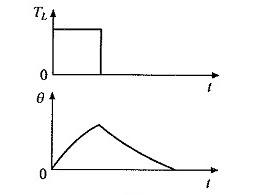
Another type of motor duty cycle is a short-time duty cycle. Time shorter than that required to reach thermal equilibrium, after running, the motor is allowed to rest to cool down up to ambient temperature.
Short time duty motors abbreviation is S2 60min. 10, 30, 60, and 90 minutes are recommended for the rated duration of the duty cycle.
S3 Intermittent Motor Duty Cycle
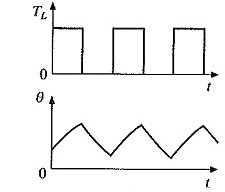
A sequence of identical duty cycles, each including a period of operation at constant load, a rest, and a de-energized period.
The duty cycle is too short for thermal equilibrium to be reached. The starting current does not significantly affect temperature rise.
S4 Intermittent duty with starting
The cycle time is too short for thermal equilibrium to be reached. In this duty type, the motor is brought to rest by the load or by mechanical braking which does not thermally load the motor.
S5 Intermittent duty with starting and electrical braking
A sequence of identical duty cycles, each cycle consisting of a significant starting period, a period of operation at constant load, a period of rapid electric braking, a rest, and a de-energized period. The time of duty cycles is too short to reach thermal equilibrium.
S6 Continuous operation periodic duty
A sequence of identical duty cycles, each cycle consisting of a period at constant load and a period of operation at no-load. The duty cycles are too short for thermal equilibrium to be reached. Recommended values for the cyclic duration factor are 15, 25, 40, and 60 percent.