Transformers are said to be connected in parallel operation when their primary connected to a common supply and secondary connected to a common load.
The function of the transformer is to deliver power to the locality, city. But in some cases, a single transformer unit is unable to fulfill the load requirement. in this case, Parallel Operation Of Transformer is preferred instead of a single transformer, multiple parallel operated transformers are installed instead of one large unit.
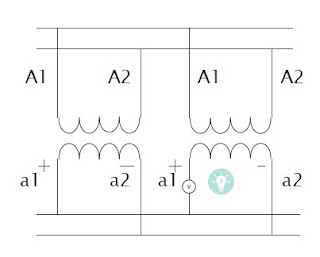
The below diagram shows the two single-phase transformers are connected in parallel, connected to the same voltage source on the primary side.
To check polarities of terminals voltmeter”v” connected in series with two secondaries. Zero voltmeter readings show proper polarities.
Using two or more transformers in parallel instead of a large single unit is uneconomical but has certain advantages.
Reasons For Parallel Operation
The reason for the parallel operation of transformers are given as follows:
1) With two or more transformers in parallel, the power becomes more reliable if one of the transformers developed a fault, it can be removed from operation and load can be supplied from the remaining transformer thought at a reduced level.
2) Parallel transformers can be switch on and off as per load demand as loads are uncertain during different times of the day.
3) The cost of the stand-by unit is much less when two or more transformers are installed.
4) As time passage the power demand increases and become more than that of the rated KVA of the existing transformer. Under such circumstances, the need for an extra transformer arises. Hence to supply such excessive demand parallel transformers are installed.
Conditions of Parallel Operation Of Transformers
Necessary Conditions for parallel operation of the transformer
- Transformers must be connected with regard to Polarity. This condition must be fulfilled strictly. If secondary terminals connected with the wrong polarity large circulating current will flow and the transformers may get damaged.
- The turn ratios of the transformer should be equal.
Desirable Conditions for parallel operation of the transformer
1) Transformers must have the same voltage ratio, this condition should satisfy as accurately as possible since different secondary voltage would give rise to undesired circulating current.
2) The equivalent impedances should be inversely proportional to the respective KVA ratings.
3) The ratio of equivalent resistance to the equivalent reactance of all transformers should be the same. If the ratio of reactance/resistance of transformer to operate in parallel are not equal, the power factor of load supplied by transformers will not be equal.
4) Per unit impedances of the transformer should be equal. If this condition is not met, the parallel operated transformers will not share the load according to their respective KVA rating. Sometimes this condition is not fulfilled by the design of the transformer in this situation, external resistances or reactances of the proper amount added in series with either the primary or secondary circuit of the transformer. where the impedance is below the value required to satisfy the condition.
Parallel operations of Three-Phase Transformers
The conditions for parallel operation of a three-phase transformer are the same as that of the single-phase transformer except for some conditions as follows.
- The phase displacement between primary and secondary voltage must be the same for all transformers to be connected in parallel.
- The phase sequence must be the same.