The dielectric strength of transformer oil is known as BDV or break-down voltage. A Transformer Oil BDV test is performed to find the dielectric strength of transformer oil.
BDV is the minimum voltage withstand the capacity of transformer oil without breakdown.
BDV test of transformer oil is very important because the transformer oil’s main function is to provide cooling and insulation between transformer core winding and the transformer body.
Oil BDV testing is necessary to determine the percentage of contamination and moisture content present in the transformer oil for the safe operation and reliability of the transformer.
Therefore, transformer oil BDV test must be carried out periodically to ensure the transformer oil’s healthiness.
The oil used in the transformer is hygroscopic that is it absorbs moisture when it comes in contact with moist air.
If oil comes in contact with moist air it absorbs moisture content from the air and its dielectric properties decrease hence BDV value also deteriorates.
The breathing air inside the transformer tank is passed through the breather, which is connected to the conservator tank. The breather is filled with silica gel crystal to absorb the moisture from the air and supply moisture-free air for the breathing of the transformer.
As per IS 6792:1992, the minimum BDV value of transformer oil shall be as follows.
1) As per IEC, the minimum BDV value of transformer oil should be 30KV at. a 2.5mm gap.
2) The Breakdown voltage after oil filtration treatment should be a minimum 70KV at a 2.5mm gap.

Why do we perform the BDV test?
Purpose of Transformer Oil BDV Test
- To predict the Residual life of the transformer
- Increase operation safety
- Increase transformer reliability
Testing Procedure
- Clean the sample valve of the transformer before taking the oil sample into the sample bottle then flush the sample bottle using transformer oil to avoid contamination of the oil
- Collect the oil sample from the bottom sample valve of the transformer into the sample bottle
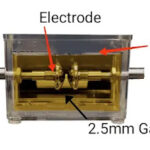
- To perform a Transformer Oil BDV Test, a BDV testing kit is used which contains a vessel that contains two electrodes mounted and separated by a 2.5mm or in some kits 4mm gap as shown in the diagram.

- Ensure the gap between electrodes is 2.5mm with the help of a 2.5mm standard GO or NO GO Gauge.
- Put the oil sample into the sample vessel of the BDV testing kit
- Keep the oil vessel open and steady for 5 min so that air bubbles if any get out.
- The oil sample for which the BDV test is to be carried out is put into the vessel and the AC voltage is applied across the two electrodes using an autotransformer and gradually increased by 2kv/sec.
- This applied AC voltage increased until the oil breakdowns, as the dielectric strength of oil breakdown. we can see the spark between two electrodes.
- The test voltage is then turned off and the voltage at which the breakdown of the dielectric strength of oil occurs is the BDV value of transformer oil.
- Repeat the same procedure six times and note down the BDV value of each test.
- Take the average of six values and this average is the BDV value of the transformer oil sample.