Types of insulation classes used in electrical motor/ transformer
There are three main categories of insulating materials, gases, liquids, and solids. The types of insulating materials are classified mainly based on thermal capability. types of insulation classes for electric motors are A, B, E, F, H, Y, and C.
Insulation is the primary thing to resist electrical stresses in electrical motors, and transformers. It should also be able to withstand other stresses that the insulation encounters during manufacture, storage, and operation.
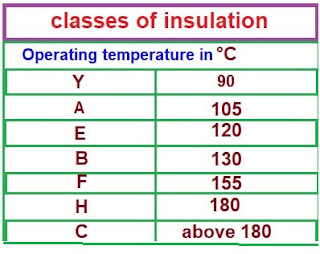
The table shows different Types of Insulation Classes
The performance of the insulation depends on its operating temperature. The higher the temperature, the higher will be the rate of its chemical degradation, and hence the lower its operating life.
if the life of insulation is expected long, its operating temperature must be maintained low i.e. in it’s operating range. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the limits of temperature for which insulation, will ensure safe operation over its expected life.
Types of insulation classes for electric motors, and transformers are classified as follows
Thus the types of AC machine insulating materials are divided into different classes A, B, and E, F, H, Y.
- CLASS ‘Y’ INSULATION – 90 ºC
- CLASS ‘A’ INSULATION – 105 ºC
- CLASS ‘E’ INSULATION – 120 ºC
- CLASS ‘B’ INSULATION – 130 ºC
- CLASS ‘F’ INSULATION – 155 ºC
- CLASS ‘H’ INSULATION – 180 ºC
- CLASS ‘C’ INSULATION – >180 ºC
Insulation Class Y: 9O°C
Withstands the temperature of up to 90°C; typically made of cotton, silk, or paper, natural rubber, polyvinyl chloride, etc. formerly O
Insulation Class A: 105°C
Class A insulation consists of materials such as cotton, silk, and paper when suitably impregnated or coated or when immersed in a dielectric liquid such as oil. Other materials or combinations of materials may be included in this class if by experience or tests, they can be shown to be capable of operation at the Class A temperature.
Insulation Class E: 12O°C
Insulation of this class has an operating temperature of 120 ºC. Insulators used for enameling of wires fall into the insulation Class E Category. e.g. PVC etc.
Insulation Class B: 13O°C
Class B insulation consists of materials or combinations of materials such as mica, glass fiber, asbestos, etc., with suitable bonding, impregnating or coating substances.
Polyethylene, terephthalate, cellulose, triacetate, polyurethanes.
Insulation Class F: 155°C
Impregnated materials, impregnated or glued with better varnishes e.g. polyurethane, epoxides, etc. fall in this category with an operating temperature of about 155 ºC
Insulation Class H: 18O°C
Class H insulation consists of materials such as silicone elastomer and combinations of materials such as mica, glass fiber, asbestos, etc.
Class B with a silicone resin binder, silicone rubber, aromatic polyamide, polyimide film, and estermide enamel.
CLASS ‘C’ INSULATION
Insulators that have operating temperatures more than 180 ºC fall in the class C insulation category. e.g. glass, ceramics, poly tera fluoro ethylene, mica etc.
All the national standards allow equipment to work up to these temperatures, but in practice, certain differentials are allowed because of the overloads, other manufacturing advantages, and economics.